Arkansas researchers screen spinach for pathogen resistance in vertical hydroponics
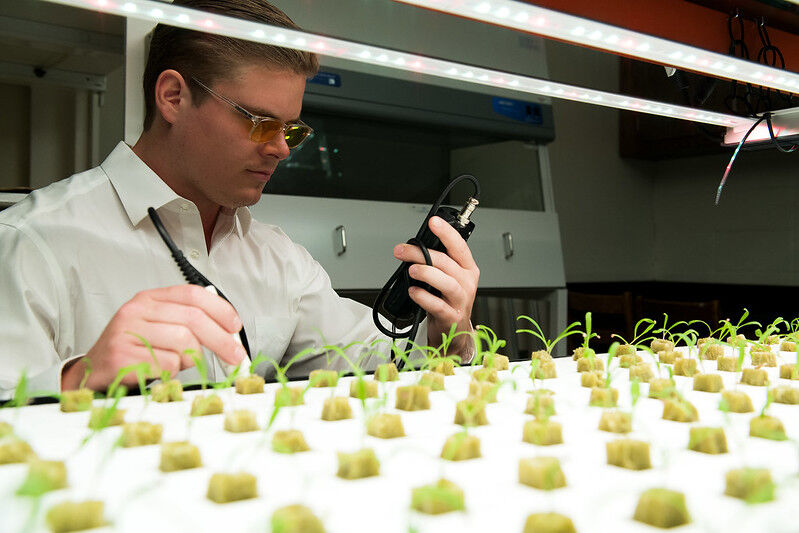

Researchers with the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station are using a new vertical farming system to find spinach varieties that have resistance to a challenging root disease in hydroponic systems.
The research is in collaboration with Bowery Farming as part of an effort to develop spinach that is resistant to Pythium. Bowery Farming states it is the largest vertical farming company in the United States in terms of retail footprint.
Pythium, a fungus-like pathogen is one of the main factors limiting the production of spinach in commercial indoor growing operations, according to Ryan Dickson, assistant professor of greenhouse and controlled-environment horticulture for the experiment station.
The experiment station is the research arm of the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture, which has a research agreement with Bowery Farming to evaluate spinach varieties for waterborne pathogen resistance. Vertical farming uses stacked hydroponic systems to increase production with a smaller footprint. A growth cycle for spinach in the system is about 21 days.
The experiments will help determine Pythium infection rates in a vertical farming system, Derek Dean, horticulture grad student, said. The vertical farming system was provided by Bowery Farming for the experiment in the department of horticulture’s McDonald Lab on the University of Arkansas campus. Garry McDonald is Dean’s academic advisor in the Dale Bumpers College Agricultural, Food and Life Sciences.
Vertical agriculture could help increase food production and expand agricultural operations as the world’s population is projected to exceed 9 billion by 2050, the article adds.
Under the bright LED grow lights and humming fans of the vertical hydroponic system provided by Bowery Farming under the agreement, Dean wears yellow-tinted safety glasses to shield his eyes as he exposes different varieties of spinach to Pythium in high and low doses. It is part of the calibration process to identify an adequate amount of Pythium to use in the experiment.